Difference between revisions of "Vermis Definition"
(Added cat.) |
|||
| (42 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | <meta name="title" content="Vermis Definition"/> | + | <!-- <meta name="title" content="Vermis Definition"/> --> |
| + | {{cer nav|vermis=true}} | ||
| + | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{h2|Vermis Definition}} | {{h2|Vermis Definition}} | ||
| + | {{TOCright}} | ||
| − | + | {{h2|Our Delineation of the Vermis: Caudal Lobules - Vermis (VIII-X)}} | |
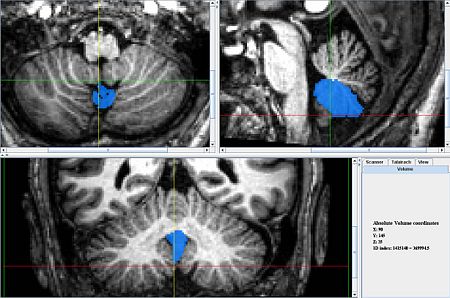
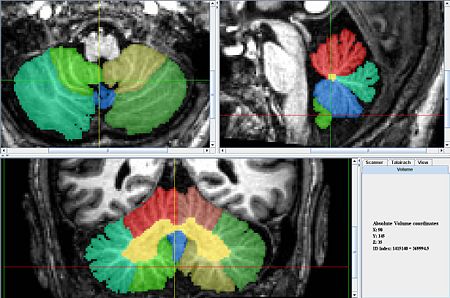
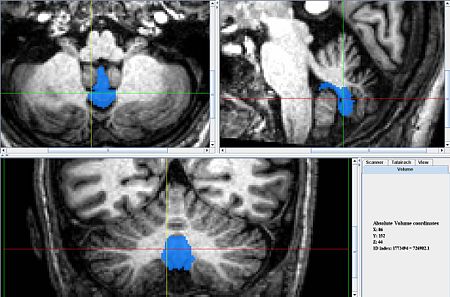
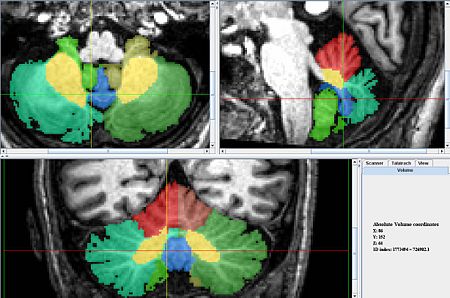
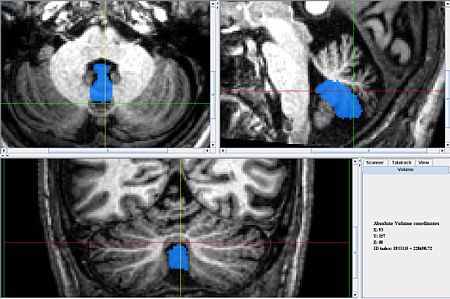
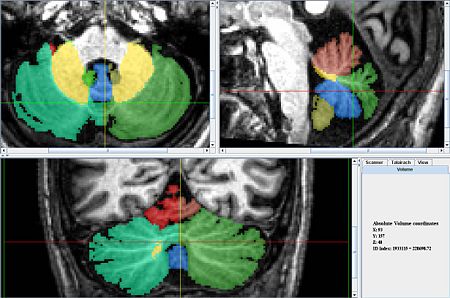
| − | == General Delineation of Vermis | + | * The vermis for the Caudal (ventral) lobes is delineated first because it is easiest to identify. It can be identified best in the sagittal view, in the anterior most and posterior most slices containing the cerebellum. In the anterior most slices it appears as a triangular shape, at the center of the cerebellum, under the narrowest portion of the vermis. In the posterior most slices it looks like a circle, somewhat detached from the other lobules, below the rest of the cerebellum. When the coronal view becomes uncertain at the center of the scan the sagittal scan can be consulted and the posterior and anterior segments connected in a way consistent with the anatomy. |
| + | |||
| + | * Coronal View | ||
| + | ** The portion of the vermis between the tonsils looks like a downward pointing triangle. | ||
| + | ** Other (more posterior) portions appear round, with arching white matter. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Later the lobules that make up this lobe of the vermis will be delineated along with all the other lobules. | ||
| + | |||
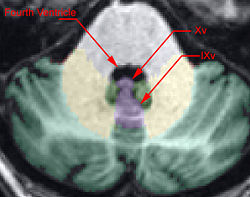
| + | * The axial view is also a useful perspective from which to delineate. Often Lobule IX vermis is easily | ||
| + | located between the tonsils (which should NOT be included in the vermis). <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Axial View | ||
| + | ** Lobule X's vermis is the anterior most portion of the vermis and appears as a round shape appearing in the same slices as the Fourth Ventricle. | ||
| + | ** Just Posterior of Xv is IXv, which is triangular, resembling an arrowhead. | ||
| + | ** Posterior of IX v is VIIIAv and VIIIBv which look like an up-turned arches. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery widths="450" heights="300"> | ||
| + | image:Vermis_blue1.jpg|Masks without hemisphere and lobe labels | ||
| + | image:Vermis_blue_all_lobes1.jpg|Masks with hemisphere and lobe labels | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery widths="450" heights="300"> | ||
| + | image:Vermis_blue2_red.jpg|Masks without hemisphere and lobe labels | ||
| + | image:vermis_blue_all_lobes2.jpg|Masks with hemisphere and lobe labels | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery widths="450" heights="300"> | ||
| + | image:Vermis_blue3_red.jpg|Masks without hemisphere and lobe labels | ||
| + | image:Vermis_blue_all_lobes3.jpeg|Masks with hemisphere and lobe labels | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery widths='250' heights="250"> | ||
| + | image:Vermis_Axial1.jpg | ||
| + | image:Vermis_Axial2.jpg | ||
| + | image:Vermis_Coronal1.jpg | ||
| + | image:Vermis_Coronal2.jpg | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery widths="300" heights="200"> | ||
| + | image:vermis9a.PNG | ||
| + | image:vermis9b.PNG | ||
| + | image:vermis9c.PNG | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{h3|Problems}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery widths="300" heights="200"> | ||
| + | image:AnonKwijibo49_vermus.jpg|The vermus can be easily delineated in the coronal view accept for the portion indicated, in that case the two sections can be connected in the sagittal view. | ||
| + | image:AnonKwijibo45_vermus_uncertain.jpg|In this scan the vermus was especially difficult to delineate because of the poor quality.Usually in the Sagittal view a distinction can be made with some certainity between lobule IX of the vermis and of the hemispheres but that distinction was unclear here. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{h2|Additional Information: General Delineation of Vermis}} | ||
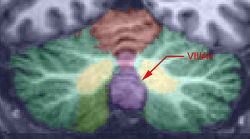
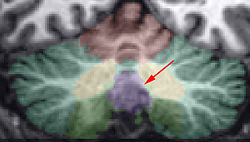
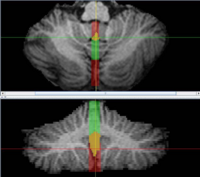
The vermis is the region of the cerebellum separating the two hemispheres, and therefore lies in the mid-sagittal slices. Once the vermis has been located, the left and right hemispheres are relatively easy to locate and label. | The vermis is the region of the cerebellum separating the two hemispheres, and therefore lies in the mid-sagittal slices. Once the vermis has been located, the left and right hemispheres are relatively easy to locate and label. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:VermisID_inf.jpg|right|thumb|300px|The Middle and Caudal Vermis]] | ||
The vermis can be located in several ways: | The vermis can be located in several ways: | ||
| Line 31: | Line 99: | ||
| − | + | {{h3|Paravermian Sulcus}} | |
| − | ---- | + | ---- |
| + | [[Image:parasulcus.PNG|right|200px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:correctvermis.PNG|right|200px]] | ||
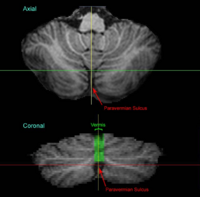
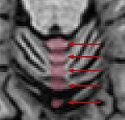
The paravermian sulcus is marked by the crosshairs in the figure below. It marks the separation of the hemispheres at the rear of the cerebellum. | The paravermian sulcus is marked by the crosshairs in the figure below. It marks the separation of the hemispheres at the rear of the cerebellum. | ||
| − | + | ||
The orange region in the figure below shows a previously labeled lobule IX_v. The green rectangles show the regions of the cerebellum that should be included in vermis labels. The red rectangles show regions that should NOT be included. | The orange region in the figure below shows a previously labeled lobule IX_v. The green rectangles show the regions of the cerebellum that should be included in vermis labels. The red rectangles show regions that should NOT be included. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 113: | ||
2. Furthermore, parts of the cerebellum that are on the edges of the paravermian sulcus should not be included in the vermal region. This is indicated by the lower (posterior) red rectangle on the axial image. | 2. Furthermore, parts of the cerebellum that are on the edges of the paravermian sulcus should not be included in the vermal region. This is indicated by the lower (posterior) red rectangle on the axial image. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{h2|Middle Lobules - Vermis (VI-VII)}} | |
| + | * UNDER CONSTRUCTION | ||
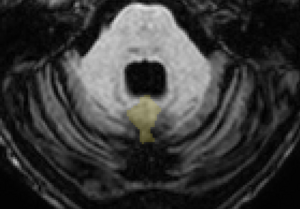
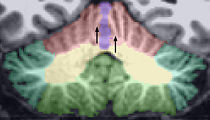
| + | [[Image:Vermis_Lob6_round.png|right|thumb|300px|Axial View of Lobule VI Vermis]] | ||
| + | The inferior most lobules in this lobe (VIIB, VIIACrusII have vermian regions resembling those of VIIIA and VIIIB). These should be delineated first. | ||
| + | Note that VIIIACrusI does NOT have a vermian region. | ||
| − | + | * Axial View | |
| + | ** VIIB and VIIACrusI look like an up-turned arches. | ||
| + | ** VI may have a rounded portion (see Figure) | ||
| − | + | * Coronal View | |
| − | |||
| − | * | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | <gallery widths | + | * Sagittal View |
| − | image: | + | ** Provides little to no information. |
| − | image: | + | |
| − | image: | + | |
| + | {{h2|Anterior Lobe Vermis (I-V) - NOT DELINEATED}} | ||
| + | [[Image:Vermis.jpg|right|thumb|300px|The Anterior Vermis - Ext]] | ||
| + | * These regions are not delineated since there are not reliable landmarks in the MR by which one can determine | ||
| + | the lateral boundaries of the vermis. | ||
| + | * Furthermore, Schmahmann says "There is no true vermis in the anterior cerebellum" <br> | ||
| + | * The below are some guidelines that may aid in this task if it is undertaken in the future. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Anterior vermis is very narrow with only subtle clues as to its boundary with the hemispheres. | ||
| + | Great care should be taken in its delineation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Axial View | ||
| + | ** Look for and include small rounded structures near the mid-sagittal plane of the cerebellum. These look like "Ice cream scoops" | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Coronal View | ||
| + | ** Look for white matter branching inward and outward and merging near the midline of the cerebellum. | ||
| + | ** The vermis exists between these branches and is at its widest near the mergers (see Figure). | ||
| + | ** Do NOT include vertically oriented white matter. Horizontal white matter may be included. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Sagittal View | ||
| + | ** Provides little to no information. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery widths="250"> | ||
| + | image:Vermis_Anterior1_arrows.jpg|The Anterior Vermis - Ice Cream Scoops | ||
| + | image:Vermis_Anterior_Coronal1_arrows.jpg|The Anterior Vermis - Fingers | ||
| + | image:Vermis_Anterior_AxialInf_arrow.jpg|Inferior part | ||
| + | image:Vermis_Anterior_Coronal2_arrows.jpg|Avoid vertically oriented gray matter | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| − | [[Category:IACL Cerebellum Pages | + | |
| + | {{h2|Cerebellar Hemispheres}} | ||
| + | Once the vermis has been delineated, the hemispheres should be given separate labels as follows: | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Lock the all vermis labels. | ||
| + | # Lock all hemisphere labels except for the anterior lobe. | ||
| + | # Paint the left hemisphere (right side of the image - CHECK HEADER!). | ||
| + | # Repeat for the caudal and middle lobes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{DEFAULTSORT:{{PAGENAME}}}} | ||
| + | [[Category:IACL]] | ||
| + | [[Category:IACL Cerebellum Pages]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:49, 3 July 2022
| Cerebellum Protocol Project | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Whole Cerebellum | Lobe Definitions | Vermis Definition | Lobule Delineation |
Vermis Definition
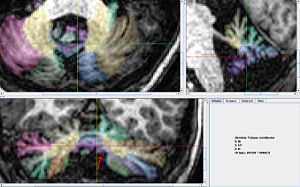
Our Delineation of the Vermis: Caudal Lobules - Vermis (VIII-X)
- The vermis for the Caudal (ventral) lobes is delineated first because it is easiest to identify. It can be identified best in the sagittal view, in the anterior most and posterior most slices containing the cerebellum. In the anterior most slices it appears as a triangular shape, at the center of the cerebellum, under the narrowest portion of the vermis. In the posterior most slices it looks like a circle, somewhat detached from the other lobules, below the rest of the cerebellum. When the coronal view becomes uncertain at the center of the scan the sagittal scan can be consulted and the posterior and anterior segments connected in a way consistent with the anatomy.
- Coronal View
- The portion of the vermis between the tonsils looks like a downward pointing triangle.
- Other (more posterior) portions appear round, with arching white matter.
- Later the lobules that make up this lobe of the vermis will be delineated along with all the other lobules.
- The axial view is also a useful perspective from which to delineate. Often Lobule IX vermis is easily
located between the tonsils (which should NOT be included in the vermis).
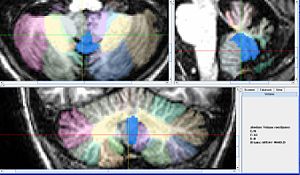
- Axial View
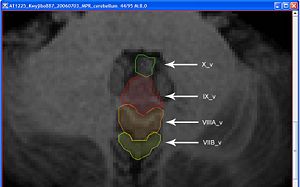
- Lobule X's vermis is the anterior most portion of the vermis and appears as a round shape appearing in the same slices as the Fourth Ventricle.
- Just Posterior of Xv is IXv, which is triangular, resembling an arrowhead.
- Posterior of IX v is VIIIAv and VIIIBv which look like an up-turned arches.
Problems
Additional Information: General Delineation of Vermis
The vermis is the region of the cerebellum separating the two hemispheres, and therefore lies in the mid-sagittal slices. Once the vermis has been located, the left and right hemispheres are relatively easy to locate and label.
The vermis can be located in several ways:
1. The vermal region of Lobule IX is nicely separate from the hemispheres and therefore can be located relatively easily (see the Lobule Identification section on Lobule IX vermis).
- In the Schmahmann book, IX_v exists (approximately) between sagittal slices X=-6 and X=+6
2. The vermis is also located by the following:
- The corpus medullare is much thinner in the vermis than in either hemisphere
- It is located in the sagittal slices near the connection of the cerebellum to the brain stem.
- Check axial and coronal views for the paravermian sulcus (see below)
3. Lobule I/II exists only in the vermal region, and therefore, any sagittal slices that contain this lobule can be considered part of the vermis
- The problem with this is that Lobule I/II is difficult to locate, and therefore finding a precise boundary of the lobule, and thereby the vermis is difficult
To best take advantage of #1, Lobule IX should be labeled first to help in locating the vermis and delineating the hemispheres and vermis (it is also easy to identify). Once IX_v has been delineated, most lobules in the same saggital slices should also carry the ‘_v’ label. However, care must be taken with the tonsils, and with lobules that span the paravermian sulcus (see below).
With the vermis located, the hemispheres can be delineated. Note that the left and right hemisphere labels should correspond the patient’s left and right.
It is therefore important to note the radiological convention – MRI images are usually oriented as though one is looking from the feet up the patient up towards the head. In this case, when viewing an axial or coronal images, the patient’s left is on the right side of the image, and vice versa. Make sure you are aware of the convention being used. To check the convention in MIPAV: Image -> Attributes -> View Header
Paravermian Sulcus
The paravermian sulcus is marked by the crosshairs in the figure below. It marks the separation of the hemispheres at the rear of the cerebellum.
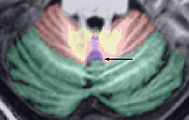
The orange region in the figure below shows a previously labeled lobule IX_v. The green rectangles show the regions of the cerebellum that should be included in vermis labels. The red rectangles show regions that should NOT be included.
1. The tonsils should not be included in the vermal region (they belong to IX_L and IX_R). This is indicated by the upper (anterior) red rectangle in the axial image and the lower (inferior) red rectangle in the coronal image. 2. Furthermore, parts of the cerebellum that are on the edges of the paravermian sulcus should not be included in the vermal region. This is indicated by the lower (posterior) red rectangle on the axial image.
Middle Lobules - Vermis (VI-VII)
- UNDER CONSTRUCTION
The inferior most lobules in this lobe (VIIB, VIIACrusII have vermian regions resembling those of VIIIA and VIIIB). These should be delineated first. Note that VIIIACrusI does NOT have a vermian region.
- Axial View
- VIIB and VIIACrusI look like an up-turned arches.
- VI may have a rounded portion (see Figure)
- Coronal View
- Sagittal View
- Provides little to no information.
Anterior Lobe Vermis (I-V) - NOT DELINEATED
- These regions are not delineated since there are not reliable landmarks in the MR by which one can determine
the lateral boundaries of the vermis.
- Furthermore, Schmahmann says "There is no true vermis in the anterior cerebellum"
- The below are some guidelines that may aid in this task if it is undertaken in the future.
The Anterior vermis is very narrow with only subtle clues as to its boundary with the hemispheres. Great care should be taken in its delineation.
- Axial View
- Look for and include small rounded structures near the mid-sagittal plane of the cerebellum. These look like "Ice cream scoops"
- Coronal View
- Look for white matter branching inward and outward and merging near the midline of the cerebellum.
- The vermis exists between these branches and is at its widest near the mergers (see Figure).
- Do NOT include vertically oriented white matter. Horizontal white matter may be included.
- Sagittal View
- Provides little to no information.
Cerebellar Hemispheres
Once the vermis has been delineated, the hemispheres should be given separate labels as follows:
- Lock the all vermis labels.
- Lock all hemisphere labels except for the anterior lobe.
- Paint the left hemisphere (right side of the image - CHECK HEADER!).
- Repeat for the caudal and middle lobes.