Difference between revisions of "Zhen"
m |
m |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
* '''Deep learning based cerebellar disease classification and functional score prediction (ongoing project)''' <br> | * '''Deep learning based cerebellar disease classification and functional score prediction (ongoing project)''' <br> | ||
| − | Dimension reduction and feature representation is | + | Dimension reduction and feature representation is an important and challenging part in studying the structral-functional relation in medical image analysis. In the past decade, deep learning has gained great attention in various fields for its power in feature learning. Here we try to apply deep learning techniques to predict cerebellar ataxia types and functional scores from MR images. Preliminary result outperforms classification method based on traditional dimension reduction techniques such as PCA. |
Revision as of 14:43, 4 February 2014
<meta name="title" content="Zhen Yang"/>
Zhen Yang
Currently I am a PhD candidate in the Image Analysis and Communications Lab (IACL) at Electrical and Computer Engineering, Johns Hopkins University. My advisor is Dr. Jerry L. Prince.
Research Interests
Medical image analysis: image segmentation, registration, statistical shape models, image based diagnosis
Computer vision: range image acquisition, registration, multi-camera calibration, feature detection and matching
Machine learning: with application to segmentation and disease classification, deep learning
Education
PhD student, 2009~present, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA
M.S., 2006~2009, Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Beijing, China
B.S., 2002~2006, Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Beijing, China
Experience
Research Assistant, Image Analysis and Communications Lab, Johns Hopkins University, 2009-present
Teaching Assistant, Medical Image Analysis, Johns Hopkins University, 2012,2013 spring
Intern, 3D Computer Vision & Graphics Group, SAMSUNG Advanced Institute of Technology, 2009 summer
Research Assistant, Laser and Vision Measurement Lab, Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2006~2009
RESEARCH PROJECTS
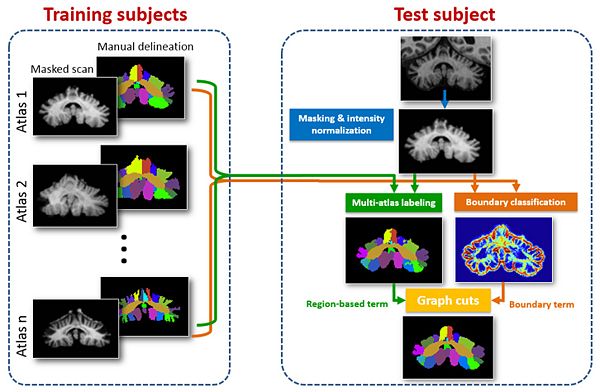
- Cerebellum sub-structure labeling
Accurate delineation of sub-regions of the cerebellum, into cerebellar lobules, is needed for studying the region specific decline in function from cerebellar pathology. In this work, we present an automated cerebellar lobule segmentation method using graph cuts, with a region-based term enforcing consistency with multi-atlas labeling results, and a boundary term defined by membership output from a random forest classifier. The automated segmentation method produces a 28 label cerebellar parcellation. It is validated using both healthy subjects and patients with cerebellar disease.
- Deep learning based cerebellar disease classification and functional score prediction (ongoing project)
Dimension reduction and feature representation is an important and challenging part in studying the structral-functional relation in medical image analysis. In the past decade, deep learning has gained great attention in various fields for its power in feature learning. Here we try to apply deep learning techniques to predict cerebellar ataxia types and functional scores from MR images. Preliminary result outperforms classification method based on traditional dimension reduction techniques such as PCA.
- Cerebellar disease type and functional score prediction in shape space
Different types of cerebellar ataxias are associated with different region-specific patterns of cerebellar atrophy. Studying these atrophy patterns can help predict disease types and stages, and in turn help treatment planning. In this work, we (1) present an automated image processing pipeline to generate a shape descriptor of the cerebellum; (2) use machine learning to predict ataxia types as well as with a cognitive score (Stroop color-word test). Using the shape descriptor as input, we are able to classify the healthy controls and different ataxia types. We also present results on predicting cognitive scores.
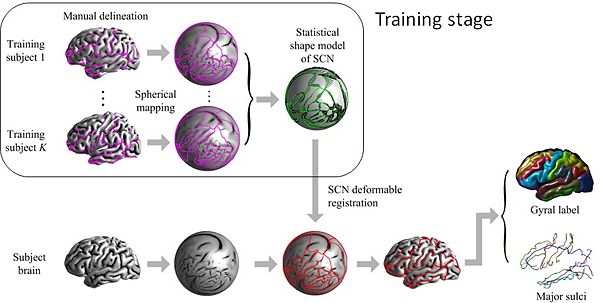
- Sulcal curve detection
Automatic labeling of the gyri and sulci on the cortical surface is important for studying cortical morphology and brain functions within populations. We propose a method to simultaneously label gyral regions and extract sulcal curves. The proposed method labels the subject cortical surface by deformably registering a network of curves that form the boundary of gyral regions to the subject cortical surface. In the registration process, the curves are encouraged to follow the fine details of the sulcal geometry and to observe the shape statistics learned from training data.
Publications
- Yang Z., Ergun E., Jedynak B., Ying S. H., Prince J. L., "Cerebellar shape analysis for cerebellar ataxia classification and functional score prediction", .Hopkins Imaging Conference 2013, Poster presentation.
- Yang Z., Bogovic J. A., Ye C., Ying S. H., Prince J. L., "Automated cerebellar lobule segmentation using graph cuts", .MICCAI Challenge Workshop on Segmentation: Algorithms, Theory and Applications (SATA) 2013, Oral and poster presentation.
- Yang Z., Carass A., Prince J. L., "Covariance shrinking in active shape models with application to gyral labeling of the cerebral cortex", .ISBI 2013, Oral presentation.
- Yang Z., Bogovic J. A., Carass A., Ye M., Searson P. C., Prince J. L., "Automatic Cell Segmentation in Fluorescence Images of Confluent Cell Monolayers Using Multi-object Geometric Deformable Model", .SPIE 2013, Oral presentation.
- Yang Z., Carass A., Prince J. L., "Automatic sulcal curve extraction with MRF based shape prior", .ISBI 2012, Oral presentation.
- Yang Z., Carass A., Chen C., Prince J. L., "Simultaneous cortical surface labeling and sulcal curve extraction", .SPIE 2012, Oral presentation.
- Yang Z., Sun J., Zhang G., "Automatic surface registration based on Regional Curvature Map", .(in Chinese), Journal of Optoelectronics • Laser (EI), 2010.
- Yang Z., Sun J., Wu Z., Zhang G., "A new camera calibration method based on two 1D targets", .(in Chinese), Journal of Optoelectronics • Laser (EI), 2010.
- Sun J., Yang Z., Liu Q., Zhang G., "Automatic and simultaneous registration of 3D measurement data", .(in Chinese), Journal of Optoelectronics • Laser (EI), 2009.
- Yang Z., Sun J., Zhang G., "Automatic registration of multi-view range images based on statistical model", .The 7th International Symposium on Instrument and Control Technology, Beijing, 2008.
Activities
- Reviewer for the Scientific World Journal.
- Reviewer for 2014 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging.
Contact
Johns Hopkins University, Homewood
Clark 204, 3400 N Charles St
Baltimore, MD 21218
Email: zyang11 at jhu dot edu